Chinese Researchers Reveal Regulatory Mechanism and Targeting Approaches of Breast Tumor-associated Macrophages
A recent study led by Dr. HU Guohong from Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health (SINH) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed the role and mechanism of miR-182 in Tumor Associated Macrophage (TAMs) of breast cancer, providing rationale for RNA-based therapeutics of TAM targeting in cancer.
Breast cancer is a major threat of woman health worldwide. Non-tumor cell components play crucial roles in cancer. Macrophages, a key component of the innate immune system that normally exert anti-tumor activities, can be educated by tumors to an alternatively activated phenotype that is known to promote tumor progression. Understanding the mechanism of macrophage education by tumor cells will help the designing of new therapeutic approaches.
In this study, researchers reported that breast tumor cells induce the expression of a microRNA, miR-182, in macrophages; while miR-182 promotes macrophage alternative activation by targeting the TLR4/NFκB signaling, leading to enhanced tumor development and progression. Importantly, using cationized mannan-modified extracellular vesicles (M-EVs) to load miR-182 inhibitors and deliver the inhibitors specifically into macrophages can effectively inhibit alternative activation of macrophages and suppress breast tumor development.
Altogether, this work highlights a role of the miR-182/TLR4/NFκB axis for tumor-induced macrophage polarization in breast cancer. Clinical analyses demonstrate the correlation of miR-182 expression and M2-like TAM infiltration in human tumor tissues. The study also provides a promising TAM-targeting RNAi strategy for cancer therapy. Further clinical studies are needed to confirm the value of miR-182 as a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target in cancer.
Entitled “miR-182 targeting reprograms tumor-associated macrophages and limits breast cancer progression”, this research was published online in PNAS on Jan 31, 2022. It was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality. Dr. HU Guohong is the corresponding author of the article and Dr. MA Chengxin is the first author. It was also supported by JIN Zi-Bing at Beijing Tongren Hospital of Capital Medical University and Dr. YING Hao at SINH.
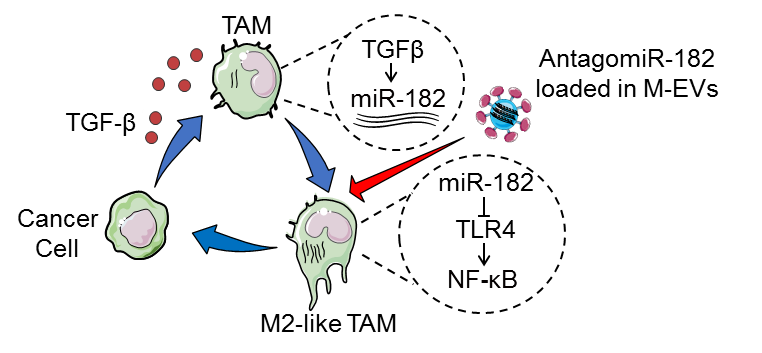
The role of miR-182 in alternative activation of breast tumor-associated macrophages and the targeting approach for cancer treatment. (Image provided by Dr. HU’s group)
Media Contact:
WANG Jin (Ms.)
Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health,
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: sibssc@sibs.ac.cn
Web: http://english.sinh.cas.cn/
