PGC-1α Activator ZLN005 Promotes Maturation of Cardiomyocytes Derived from Human Embryonic Stem Cells
A recent study published online in Aging revealed a novel role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) activator ZLN005 in the promoting maturation of cardiomyocytes differentiated from human embryonic stem cells (hESC-CMs). The findings would facilitate the application of hESC-CMs in the areas of disease modeling, drug screening, and engineering cardiac tissue.
The study was conducted by research teams led by Dr. YANG Huangtian from Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health (SINH) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Dr. LU Xiyuan from Institute for Fetology of First Hospital of Soochow University.
Human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hPSC-CMs) have great potential in biomedical applications. However, the immature state of cardiomyocytes obtained using existing protocols limits the application of hPSC-CMs. Several approaches have been reported to enhance hPSC-CMs’ maturation, such as long-term culture, bioelectrical stimulation, mechanical stretch, biochemical stimulation, and the incorporation of CMs into 3D tissue constructs. However, these methods are limited by time consuming, expensive, and technically challenging, which are not suitable for widespread adoption.
Unlike adult cardiac myocytes, hPSC-CMs generate ATP through an immature metabolic pathway, aerobic glycolysis, instead of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Hence, metabolic switching is critical for functional maturation in hPSC-CMs. PGC-1α is a key regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis and metabolism, which may help promote cardiac maturation during development.
In this study, researchers investigated the effects of PGC-1α and its activator ZLN005 on the maturation of hESC-CM. hESC-CMs were generated using a chemically defined differentiation protocol and supplemented with either ZLN005 or DMSO (control) on differentiating days 10 to 12. Biological assays were then performed around day 30. ZLN005 treatment upregulated the expressions of PGC-1α and mitochondrial function-related genes in hESC-CMs and induced more mature energy metabolism compared with the control group. In addition, ZLN005 treatment increased cell sarcomere length, improved cell calcium handling, and enhanced intercellular connectivity.
These findings provide an effective approach to promote hESC-CM maturation, which is critical for the application of hESC-CM in disease modeling, drug screening, and engineering cardiac tissue.
The study entitled “PGC-1α activator ZLN005 promotes maturation of cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells” was published online in Aging on Apr. 28, 2020. The research was supported by Dr. LIANG Ping and his team members from the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University and was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key R&D Program of China, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the CAS, and Postdoctoral Fellowship from NIH.
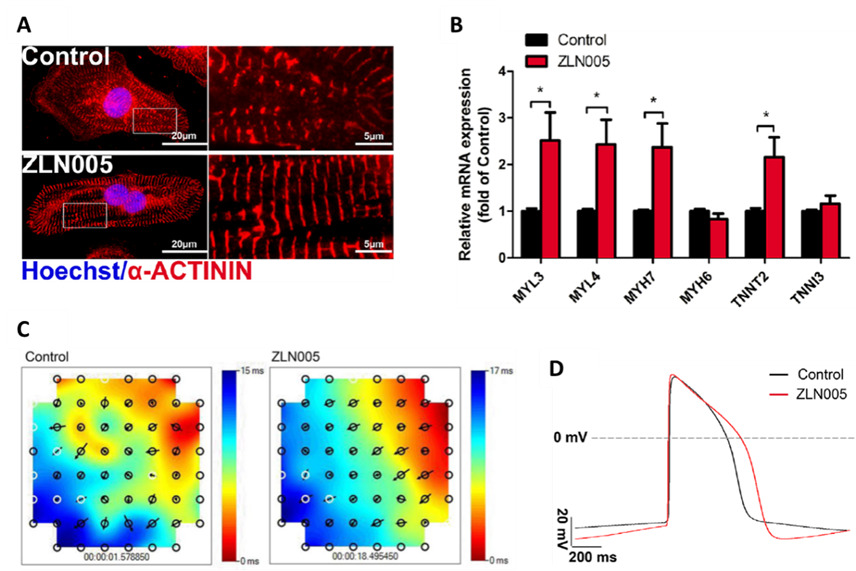
ZLN005 promotes maturation of cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells in different aspects. (Image by Dr. LU Xiyuan, Dr. YANG Huangtian and Dr. LIANG Ping's Groups)
Media Contact:
WANG Jin (Ms.)
Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health,
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: sibssc@sibs.ac.cn
