Researchers Reveal Therapeutic Effect of Compound Kushen Injection Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma
A recent study led by Dr. WANG Hui’s group from Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health (SINH) of Chinese Academy of Sciences and School of Public Health, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine reveals the role of Compound kushen injection (CKI) in remodeling hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) immune microenvironment and sensitizing HCC to sorafenib, thus providing new therapeutic strategy for HCC.
HCC is the most common malignant primary liver cancer with limited effective treatments, ranking as the fourth cause of cancer-related death globally. Sorafenib is the first frontline chemotherapeutic drug to treat advanced HCC. However, only 30% of HCC patients can benefit from sorafenib due to severe adverse effects, acquired resistance, tumor heterogeneity, and an immunosuppressive microenvironment. As a promising treatment for cancer, immunotherapy has been investigated as an option for HCC treatment. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) is closely involved in tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment formation to promote HCC initiation, growth, and metastasis. Thus, targeting TAMs to remodel tumor microenvironment has been a potential strategy for HCC treatment.
CKI is a traditional Chinese medicine formula approved by National Medical Products Administration to treat cancer-induced pain in clinical for over 25 years. However, the effect of CKI on HCC growth and HCC immune microenvironment is still unknown. In this study, researchers reported that CKI suppresses the tumor growth of HCC and improves the therapeutic outcomes of low-dose sorafenib in vivo, which avoids sorafenib-induced adverse chemotherapy effects. Meanwhile, CKI combined with low-dose sorafenib also reducestumor recurrence and elicits a long-term antitumor memory response against HCC. Furthermore, CKI decreases the distribution of M2-TAMs, promotes the proportion of M1-TAMs and CD8+ T cells in the tumor tissues and subsequently reshapes the HCC immune microenvironment.
Mechanism study revealed that CKI acts on macrophages to facilitate the formation of TNFR1/TRADD/RIP1/TRAF2 complex and trigger downstream NF-κB p65 and MAPK p38 pathways which play pro-inflammatory roles, tunes TAMs status towards anti-tumor M1-TAMs activation, and reverses the polarization of pro-tumor M2-TAMs. CKI-primed macrophages further promote the proliferation and tumor-killing activity of CD8+ T cells to induce HCC cells apoptosis, protect functional CD8+ T cells from exhaustion to maintain anti-HCC immunologic memory activity, and finally suppress HCC tumor growth and recurrence.
Overall, this study shows that traditional Chinese medicines with immunomodulatory properties can potentiate chemotherapeutic drugs and provide new promising approaches for HCC treatment.
This work entitled “Compound kushen injection relieves tumor-associated macrophage-mediated immunosuppression through TNFR1 and sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib” was published online in Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer on March 15, 2020. PhD student Mr. YANG Yang from SINH is the first author, and Dr. WANG Hui, Dr. BA Qian and Dr. YANG Chenghua are the co-corresponding authors of this publication. The study was funded by the grants from National Key R&D Program of China.
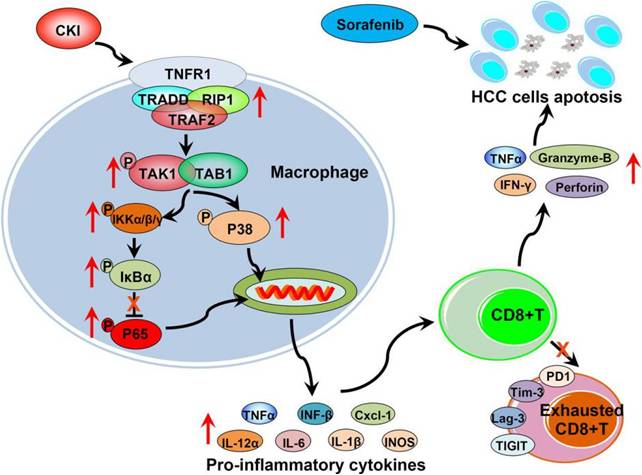
Schematic depiction of the reconstruction of HCC immune microenvironment by CKI and its therapeutic effects when combined with sorafenib. (Image provided by Dr. WANG Hui’s group)
Media Contact:
WANG Jin (Ms.)
Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health,
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: sibssc@sibs.ac.cn
