Scientists Discover the Crosstalk Between ILC3s and Tregs Through OX40L-OX40 Interaction in the Intestine
Maintaining the healthy physical quality depends largely on a perfect immune system, which includes a variety of adaptive and innate immune cells and their functional crosstalks. As a member of adaptive immune system, regulatory T cells (Treg cells) are important for preventing the incidence and progression of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s diseases and ulcerative colitis. Identifying cellular and molecular pathways to maintain Treg homeostasis could provide new insights for the immunotherapy of these diseases.
OX40 is constitutively expressed by Tregs and is critical for the development and maintenance of Tregs. OX40 ligand (OX40L) has been found to be expressed by mouse splenic lymphoid tissue inducer (Lti) cells and ILC3s in the meninges. Whether ILC3s serve as sources of intestinal OX40L, or their crosstalk with Tregs in the intestine through OX40L, has not been reported so far.
Recently, Dr. QIU Ju’s group from Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health of Chinese Academy of Sciences found that group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s)-derived OX40L was essential for homeostasis of intestinal Tregs. The study entitled "ILC3-derived OX40L is essential for homeostasis of intestinal Tregs in immunodeficient mice" has been published online in Cellular & Molecular Immunology on Feb. 13th, 2019. ( https://www.nature.com/articles/s41423-019-0200-x)
In this work, researchers showed that ILC3s were the major source of OX40L among intestinal leukocytes, and Inflammation triggered OX40L expression. Poly(I:C) representing viral stimulus promoted OX40L expression in ILC3s via a cell-autonomous manner, indicating that ILC3 might participate in the response to viral infection.
Moreover, researchers found that CD4+ T cells suppressed OX40L expression on ILC3s through the expression of OX40. Mechanistically, IL-7-STAT5 signaling sustained the OX40L expression by intestinal ILC3s.
Finally, researchers revealed that ILC3-derived OX40L was essential for Treg homeostatic expansion in the intestine. Furthermore, they found the ILC3-Treg co-localized in the intestinal cryptopatches, indicating the supportive role of ILC3-derived OX40L on Tregs in the intestine through a direct interaction with OX40 expressed by Tregs.
The crosstalk of intestinal ILC3s and Tregs through OX40L-OX40 revealed by this work provides valuable basis for potential therapeutic strategies of IBD and other autoimmune diseases.
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China, Ministry of Science and Technology, and Chinese Academy of Sciences.
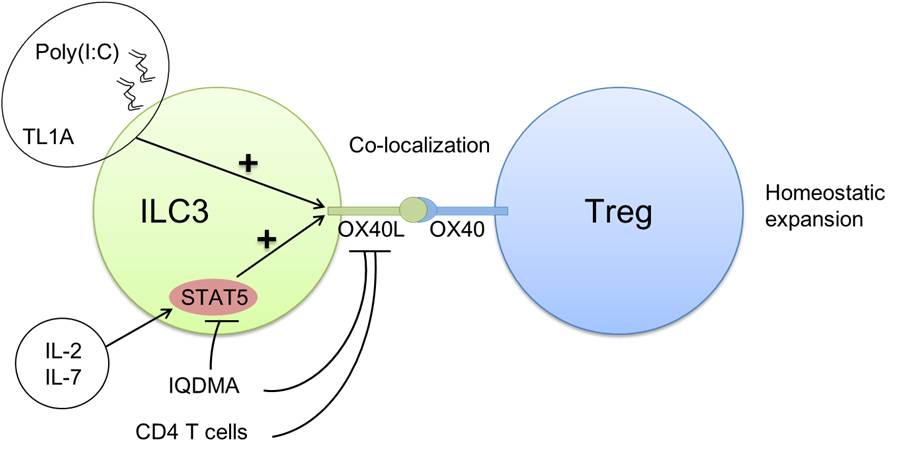
Schematic illustration of the regulation of OX40L expression by ILC3 and its supportive role on intestinal Tregs homeostasis.
(Image by Dr. Qiu Ju's group)
Media Contact:
WANG Jin (Ms.)
Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health,
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: sibssc@sibs.ac.cn
