Researchers Identify Lipid Peroxidation as a Prominent Feature in Human Plasma of Patients with Coronary Heart Diseases
Researchers led by Dr.YINHuiyong, from Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences (SIBS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and Dr. Lemin ZHENG, from Peking University Health Science Center has identified oxidative stress-induced lipid peroxidation (LPO) is a prominent feature in coronary heart diseases (CHD) and LPO metabolites have the potential to differentiate different stages of CHD once validated in larger cohorts.
CHD, one of the leading causes of death in the world, is characterized by the formation of atherosclerotic plaques inside the coronary arteries. Over time, the plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, reducing or blocking the blood flow to the heart, leading to angina or myocardial infarction (MI). CHD is a complex metabolic disorder but the underlying mechanisms and diagnostic biomarkers for the different stages of CHD remain poorly defined.
Metabolomics is a powerful technique to systematically study the entire metabolites and metabolic pathways in a given biological system and has been increasingly employed to identify metabolic biomarkers and improve clinical diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
In this study, the team performed plasma metabolomics to investigate the metabolic changes associated different stages of CHD. Subsequent analysis demonstrated a uniquely altered metabolic profile in different stages of CHD and a series of potential differential metabolites were identified.
Pathway analysis revealed that glycerophospholipid (GPL) metabolism emerged as the most significantly disturbed pathway. Next, the researchers used a targeted lipidomics approach to analyze GPL metabolites including oxidized phospholipid (oxPL) and downstream metabolites derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs).
The results showed that LPO metabolites including oxPLs and isoprostanes were significantly elevated in plasma of MI patients comparing to healthy control (HC) and stable angina (SA), consistent with the notion that oxidative stress-induced LPO is a prominent feature in CHD, implying LPO metabolites may serve as potential biomarkers to differentiation MI from SA and HC.
The study entitled “Comprehensive Metabolomics Identified Lipid Peroxidation as A Prominent Feature in Human Plasma of Patients with Coronary Heart Diseases” was published online in Redox Biology on April 26th, 2017. A Ph.D. graduate student Ms. LU Jianhong and Dr. CHEN Buxing were the co-leading authors for this study.
This study was collaborated with Dr. CHEN Buxing at Department of Cardiology, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, and Dr. ZHU Zhengjiang at Interdisciplinary Research Center on Biology and Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The work was financially supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Ministry of Science and Technology of China.
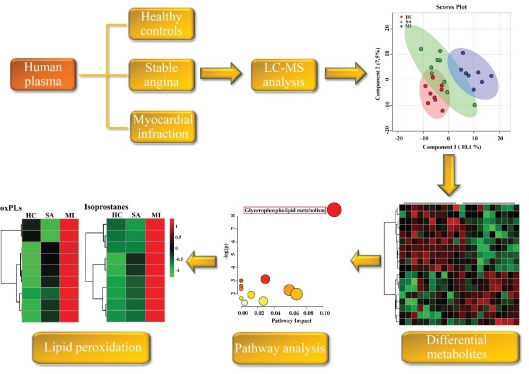
Graphical abstract: Overview of metabolomic and lipidomics characterization of different stages of CHD.
(Image provided by Dr. YIN Huiyong’s group)
Correspondence:
YIN Huiyong, Ph.D., Principal Investigator
Key Laboratory of Food Safety Research, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences
320 Yueyang Road, Shanghai, China
E-mail: hyyin@sibs.ac.cn
