Multifunctional Degradation Enzymes and Functional Biomaterials Obtained for Control of Mycotoxins Contaminated Concerning Food Safety
Novel strategies with highly efficient degradation without safety concerns for control of mycotoxins contaminated in food and feed stuffs are aroused with increasingly interests, either from research or from public levels in recent decades worldwide.
As convinced before, the specific enzymes are generally used for degradation of individual mycotoxins, exemplified with zearalenone (ZEN) and ochratoxin A (OTA). Realistically, ZEN and OTA are always co-occurring in nature, especially in the samples of cereal grains and derived feeds. Thus, the needs for multifunctional enzymes with simultaneous degradation of ZEN and OTA are really welcome in practical uses.
To attain this purpose, Dr. WU Aibo's group from Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health of Chinese Academy of Sciences first obtained the fusion gene with the reported single genes after codon optimization for ZEN and OTA, respectively. And then plasmid construction, protein expression and purification and enzymatic assays were performed to get the final recombinant enzymes. Finally, the enzymes were capable to completely degrade ZEN in 2 h and OTA in 30 min, under the good conditions of pH 7, 35℃ and 30℃, respectively.
On the other hand, biological control of mycotoxin-producing phytopathogens and derived mycotoxins is more and more favorable, due to its original and low-cost operation. Previously through large-scale screening, researchers acquired one fungal isolate of Trichoderma harzianum with the above mentioned capabilities. Then they prepared the biomaterials of Trichoderma harzianum-derived Selenium Nanoparticles, with the expected functionalities. As confirmed, these nanomaterials could substantially inhibit the growth of various fungi, and reduce the production levels of main mycotoxins, such as Alternaria toxins (83% of TeA, and 79% of AOH reduction) and Fumonisin B1 (63% of FB1 reduction).
The achieved multifunctional degradation enzymes and biogenic nanoparticles are applicable with great potential for control of mycotoxins contaminated in the whole food chain. Also, the proposed novel strategy there would be valuable references for food safety management, especially at the industrial levels.
The research results have been published on the journals of Toxins and Food control, which were financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Chinese Academy of Sciences.
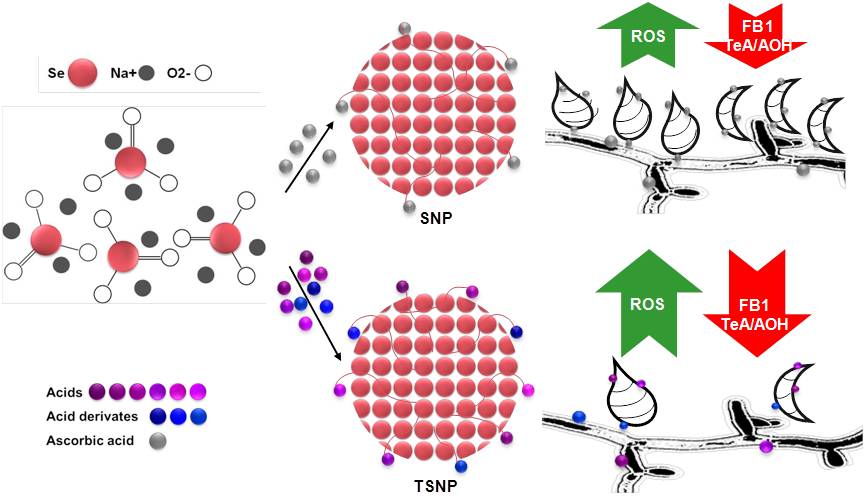
The obtained biogenic nanoparticles for simultaneous control on growth of phytopathogens and mycotoxins productions. (Image by Dr. WU Aibo's Group)
Media Contact:
WANG Jin (Ms.)
Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health,
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: sibssc@sibs.ac.cn
